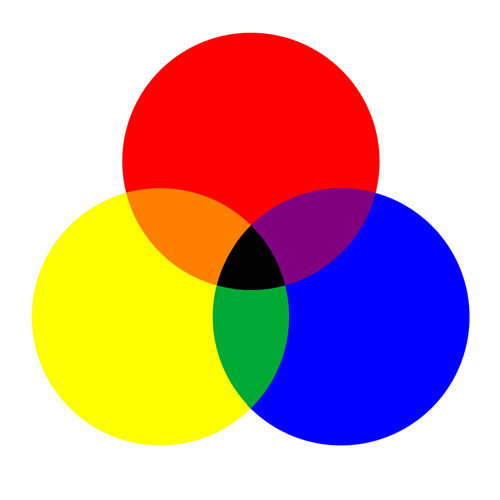
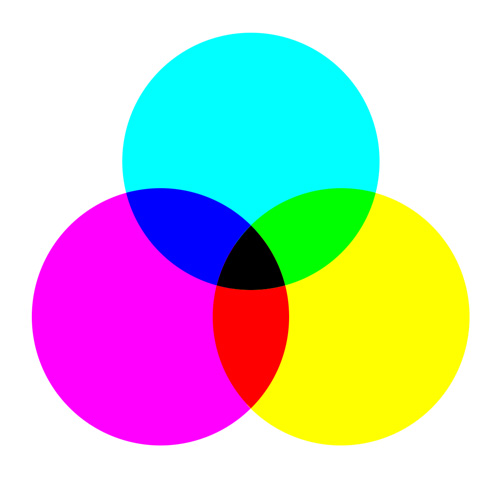
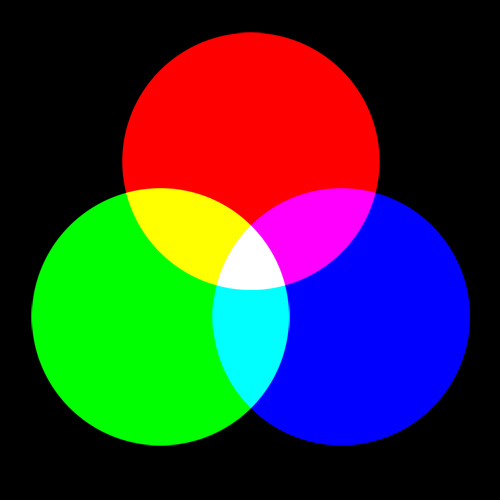
You have two choices with this lesson, watch me discuss the issue in
the video below, or read the full text.
This site is ©2026 by Neil Blevins, All rights
are reserved.
To see hundreds of other tutorials similar to this one, visit the
Neil Blevins Education Site